Isaac Newton
Lived 1643 to 1727.
Isaac Newton is perhaps the greatest physicist who has ever lived. He and Albert Einstein are almost equally matched contenders for this title.
Each of these great scientists produced dramatic and startling transformations in the physical laws we believe our universe obeys, changing the way we understand and relate to the world around us.
Early Life and Education
Isaac Newton was born on January 4, 1643 in the tiny village of Woolsthorpe-by-Colsterworth, Lincolnshire, England.
His father, whose name was also Isaac Newton, was a farmer who died before Isaac Junior was born. Although comfortable financially, his father could not read or write.
His mother, Hannah Ayscough, married a churchman when Newton was three years old.
Newton disliked his mother’s new husband and did not join their household, living instead with his mother’s mother, Margery Ayscough.
His resentment of his mother and stepfather’s new life did not subside with time; as a teenager he threatened to burn their house down!
Beginning at age 12, Newton attended The King’s School, Grantham, where he was taught the classics, but no science or mathematics. When he was 17, his mother stopped his schooling so that he could become a farmer. Fortunately for the future of science Newton found he had neither aptitude nor liking for farming; his mother allowed him to return to school, where he finished as top student.
Servant and Undergraduate
In June 1661, aged 18, Newton began studying for a law degree at Cambridge University’s Trinity College, earning money working as a personal servant to wealthier students.
By the time he was a third-year student he was spending a lot of his time studying mathematics and natural philosophy (today we call it physics). He was also very interested in alchemy, which we now categorize as a pseudoscience.
His natural philosophy lecturers based their courses on Aristotle’s incorrect ideas from Ancient Greece. This was despite the fact that 25 years earlier, in 1638, Galileo Galilei had published his physics masterpiece Two New Sciences establishing a new scientific basis for the physics of motion.
Newton began to disregard the material taught at his college, preferring to study the recent (and more scientifically correct) works of Galileo, Boyle, Descartes, and Kepler. He wrote:
 “Plato is my friend, Aristotle is my friend, but my greatest friend is truth.”
“Plato is my friend, Aristotle is my friend, but my greatest friend is truth.”
ISAAC NEWTON
Mathematician and Physicist
Reading the works of these great scientists, Newton grew more ambitious about making discoveries himself. While still working part-time as a servant, he wrote a note to himself. In it he posed questions which had not yet been answered by science. These included questions about gravity, the nature of light, the nature of color and vision, and atoms.
After three years at Cambridge he won a four-year scholarship, allowing him to devote his time fully to academic studies.
A Mind on Fire
In 1665, at the age of 22, a year after beginning his four-year scholarship, he made his first major discovery: this was in mathematics, where he discovered the generalized binomial theorem. In 1665 he was also awarded his B.A. degree.
By now Newton’s mind was ablaze with new ideas. He began making significant progress in three distinct fields – fields in which he would make some of his most profound discoveries:
- calculus, the mathematics of change, which is vital to our understanding of the world around us
- gravity
- optics and the behavior of light
He did much of his work on these topics back home at Woolsthorpe-by-Colsterworth after the Great Plague forced his college in Cambridge to close.
Fellow and Lucasian Professor of Mathematics
At the age of 24, in 1667, he returned to Cambridge, where events moved quickly.
First he was elected as a fellow of Trinity College.
A year later, in 1668, he was awarded an M.A. degree.
A year after that, the Lucasian Professor of Mathematics at Trinity College, Isaac Barrow, resigned and Newton was appointed as his replacement; he was just 26 years old. Barrow, who had recommended that Newton should succeed him, said of Newton’s skills in mathematics:
 “Mr Newton, a fellow of our College, and very young, being but the second year master of arts; but of an extraordinary genius and proficiency.”
“Mr Newton, a fellow of our College, and very young, being but the second year master of arts; but of an extraordinary genius and proficiency.”
ISAAC BARROW
Mathematician
Isaac Newton’s Scientific Achievements and Discoveries
Achievements in Brief
Isaac Newton, who was largely self-taught in mathematics and physics:
- generalized the binomial theorem
- showed that sunlight is made up of all of the colors of the rainbow. He used one glass prism to split a beam of sunlight into its separate colors, then another prism to recombine the rainbow colors to make a beam of white light again.
- built the world’s first working reflecting telescope.
- discovered/invented calculus, the mathematics of change, without which we could not understand the behavior of objects as tiny as electrons or as large as galaxies.
- wrote the Principia, one of the most important scientific books ever written; in it he used mathematics to explain gravity and motion. (Principia is pronounced with a hard c.)
- discovered the law of universal gravitation, proving that the force holding the moon in orbit around the earth is the same force that causes an apple to fall from a tree.
- formulated his three laws of motion –Newton’s Laws – which lie at the heart of the science of movement.
- showed that Kepler’s laws of planetary motion are special cases of Newton’s universal gravitation.
- proved that all objects moving through space under the influence of gravity must follow a path shaped in the form of one of the conic sections, such as a circle, an ellipse, or a parabola, hence explaining the paths all planets and comets follow.
- showed that the tides are caused by gravitational interactions between the earth, the moon and the sun.
- predicted, correctly, that the earth is not perfectly spherical but is squashed into an oblate spheroid, larger around the equator than around the poles.
- Used mathematics to model the movement of fluids – from which the concept of aNewtonian fluid comes.
- devised Newton’s Method for finding the roots of mathematical functions.
 A cylinder of air reaching to the top of the atmosphere is of equal weight with a cylinder of water about 33 feet high.
A cylinder of air reaching to the top of the atmosphere is of equal weight with a cylinder of water about 33 feet high.
ISAAC NEWTON
Some Details about Newton’s Greatest Discoveries
Newton revealed his laws of motion and gravitation in his book the Principia. Just as few people at first could understand Albert Einstein’s general theory of relativity, few people understood the Principia when it was published. When Newton walked past them one day, one student remarked to another:
“There goes a man who has written a book that neither he nor anybody else understands.”
Newton’s ideas were spread by the small number of people who understood the Principia, and who were able to convey its message in more accessible ways: people including Leonard Euler, Joseph Louis Lagrange, Pierre Simon de Laplace, Willem Jacob ‘s Gravesande, William Whiston, Voltaire, John Theophilus Desaguliers, and David Gregory.
Calculus
Newton was the first person to fully develop calculus. Calculus is the mathematics of change. Modern physics and physical chemistry would be impossible without it. Other academic disciplines such as biology and economics also rely heavily on calculus for analysis.
In his development of calculus Newton was influenced by Pierre de Fermat, who had shown specific examples in which calculus-like methods could be used. Newton was able to build on Fermat’s work and generalize calculus. Newton wrote that he had been guided by:
 “Monsieur Fermat’s method of drawing tangents.”
“Monsieur Fermat’s method of drawing tangents.”
ISAAC NEWTON
Mathematician and Physicist
From Newton’s fertile mind came the ideas that we now call differential calculus, integral calculus and differential equations.
Soon after Newton generalized calculus, Gottfried Leibniz achieved the same result. Today, most mathematicians give equal credit to Newton and Leibniz for calculus’s discovery.
Universal Gravitation and the Apple
 Newton’s famous apple, which he saw falling from a tree in the garden of his family home in Woolsthorpe-by-Colsterworth, is not a myth.
Newton’s famous apple, which he saw falling from a tree in the garden of his family home in Woolsthorpe-by-Colsterworth, is not a myth.
He told people that seeing the apple’s fall made him wonder why it fell in a straight line towards the center of our planet rather than moving upwards or sideways.
Ultimately, he realized and proved that the force behind the apple’s fall also causes the moon to orbit the earth; and comets, the earth and other planets to orbit the sun. The force is felt throughout the universe, so Newton called it Universal Gravitation. In a nutshell, it says that mass attracts mass.
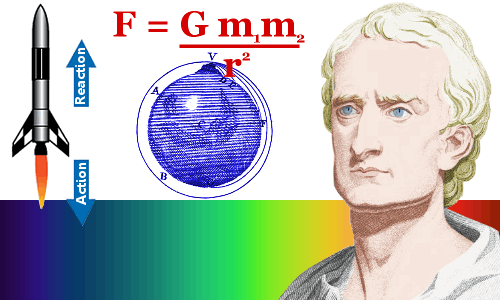
Newton discovered the equation that allows us to calculate the force of gravity between two objects.
Most people don’t like equations much: E = mc2 is as much as they can stand, but, for the record, here’s Newton’s equation:
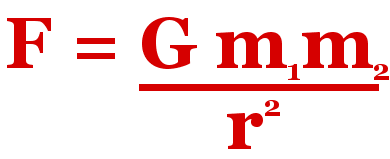
Newton’s equation says that you can calculate the gravitational force attracting one object to another by multiplying the masses of the two objects by the gravitational constant and dividing by the square of the distance between the objects.
Dividing by distance squared means Newton’s Law is an inverse-square law.
Newton proved mathematically that any object moving in space affected by an inverse-square law will follow a path in the shape of one of the conic sections, the shapes which fascinated Archimedesand other Ancient Greek mathematicians.
For example, planets follow elliptical paths; while comets follow elliptical, or parabolic or hyperbolic paths.
And that’s it!
Newton showed everyone how to calculate the force of gravity between things such as people, planets, stars and apples.
Newton’s Laws of Motion

Third Law: The rocket flies because of the upward thrust it gets in reaction to the high speed gas particles pushing downward from its engines.
First law: Objects remain stationary or move at a constant velocity unless acted upon by an external force. This law was actually first stated by Galileo, whose influence Newton mentions several times in the Principia.
Second law: The force F on an object is equal to its mass m multiplied by its acceleration: F = ma.
Third law: When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts a force equal in size and opposite in direction on the first object.
With Newton’s calculus, universal gravitation, and laws of motion, you have enough knowledge at your fingertips to plot a course for a spaceship to any planet in our solar system or even another solar system!
And Isaac Newton figured it all out about 300 years before we actually did send a spaceship to the planets.
A Word of Caution
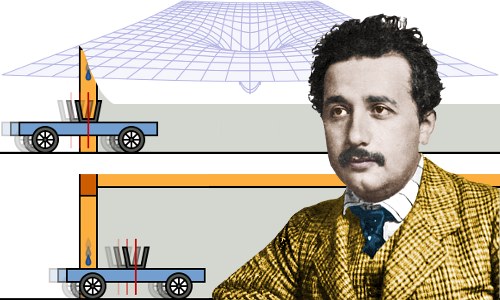
Newton’s laws become increasingly inaccurate when speeds reach substantial fractions of the speed of light, or when the force of gravity is very large. Einstein’s equations are then required to produce reliable results.
Newton’s laws become increasingly inaccurate when speeds reach substantial fractions of the speed of light, or when the force of gravity is very large. Einstein’s equations are then required to produce reliable results.
Optics and Light
Newton was not just clever with his mind. He was also skilled in experimental methods and working with equipment.
He built the world’s first reflecting telescope. This telescope focuses light from a curved mirror. Reflecting telescopes have several advantages over earlier telescopes including:
- they are cheaper to make
- they are easier to make in large sizes, gathering more light, allowing higher magnification
- they do not suffer from a focusing issue associated with lenses called chromatic aberration.
Newton also used glass prisms to establish that white light is not a simple phenomenon. He proved that it is made up of all of the colors of the rainbow, which could recombine to form white light again.
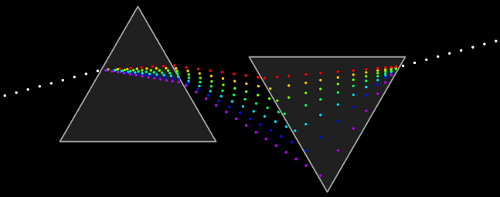
Newton’s crucial 1672 experiment with two prisms. The result absolutely demolished competing theories, such as the proposal that glass added the colors to sunlight.
Alchemy, Feuds, Religion, and Planets Orbiting Distant Stars
Although he is one of the greatest scientists in history, Newton’s laboratory papers show that he probably devoted more of his time to alchemy than to anything we would recognize as science.
Not surprisingly, Newton never found the Philosophers’ Stone. Given his towering contributions to real science, all we can do is wonder what else he might have achieved if he had not been such a passionate alchemist.
Despite his brilliance, Newton was a very insecure man: most historians trace this back to his childhood family difficulties.
Newton published very little work until his later years, because in his early years as a scientist,Robert Hooke had disagreed strongly with a scientific paper Newton had published. Newton took criticism of his work in a very personal way and developed a lifelong loathing for Hooke.
His lack of published work also caused a huge issue when Gottfried Leibniz starting publishing his own version of calculus. Newton was already a master of this branch of mathematics, but had published very little of it. Again Newton’s insecurity got the better of him, and he angrily accused Leibniz of stealing his work. The pros and cons of each man’s case have long been debated by historians. Most mathematicians regard Newton and Leibniz as equally responsible for the development of calculus.
Newton was a very religious man with somewhat unorthodox Protestant Christian views. He spent a great deal of time and wrote a large body of private works concerned with theology and his interpretation of the Bible.
His scientific work had revealed a universe that obeyed logical mathematical laws. He had also discovered that starlight and sunlight are the same, and he speculated that stars could have their own systems of planets orbiting them. He believed such a system could only have been made by God.
 This most beautiful system of the sun, planets and comets could only proceed from the counsel and dominion of an intelligent and powerful Being. And if the fixed stars are the centers of other like systems, these, being formed by the like wise counsel, must be all subject to the dominion of One; especially since the light of the fixed stars is of the same nature with the light of the sun.
This most beautiful system of the sun, planets and comets could only proceed from the counsel and dominion of an intelligent and powerful Being. And if the fixed stars are the centers of other like systems, these, being formed by the like wise counsel, must be all subject to the dominion of One; especially since the light of the fixed stars is of the same nature with the light of the sun.
ISAAC NEWTON
Moving On
In 1696, Newton was appointed as a Warden of the Royal Mint. In 1700, he became Master of the Mint, leaving Cambridge for London, and more or less ending his scientific discovery work. He took his new role very seriously, going out into London’s taverns in disguise gathering evidence against counterfeiters.
In 1703, he was elected President of the Royal Society.
In 1705, he was knighted, becoming Sir Isaac Newton.
 “Nature to Newton was an open book, whose letters he could read without effort.”
“Nature to Newton was an open book, whose letters he could read without effort.”
ALBERT EINSTEIN
Theoretical Physicist
The End
Isaac Newton died on March 31, 1727, aged 84. He had never married and had no children.
He was buried in Westminster Abbey, London.